[ad_1]
Key Takeaways
- M&A activity in the cybersecurity sector is on pace to exceed 2024 volume by 10% in 2025, with continued consolidation as larger firms acquire niche players to enhance capabilities or expand product offerings.
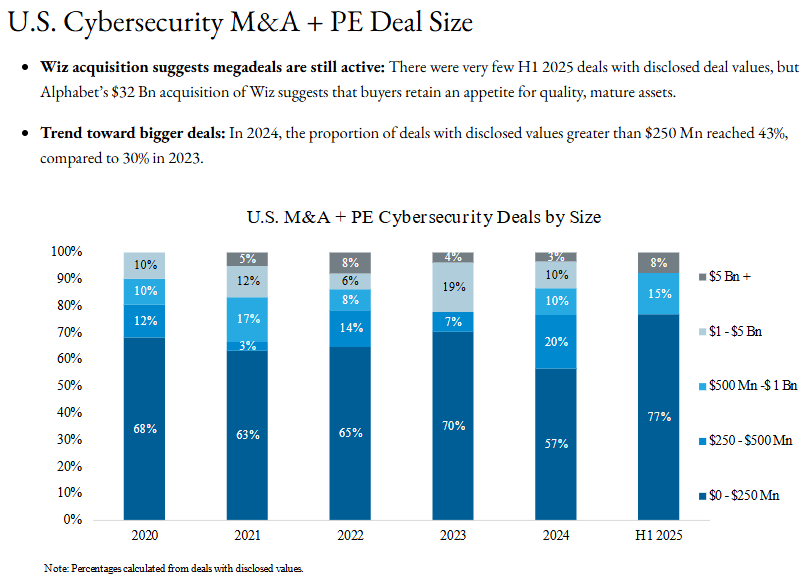
- The cybersecurity sector is experiencing a trend toward larger transactions, with a rising proportion of deals over $250 million, as both strategic buyers and private equity investors focus on acquiring high-quality, mature assets to build comprehensive platforms and address the growing complexity of cyber threats.
- The integration of generative and agentic AI is accelerating innovation in threat detection and automation, while heightened regulatory and geopolitical factors are shaping deal structures and strategic decisions across the cybersecurity M&A landscape.
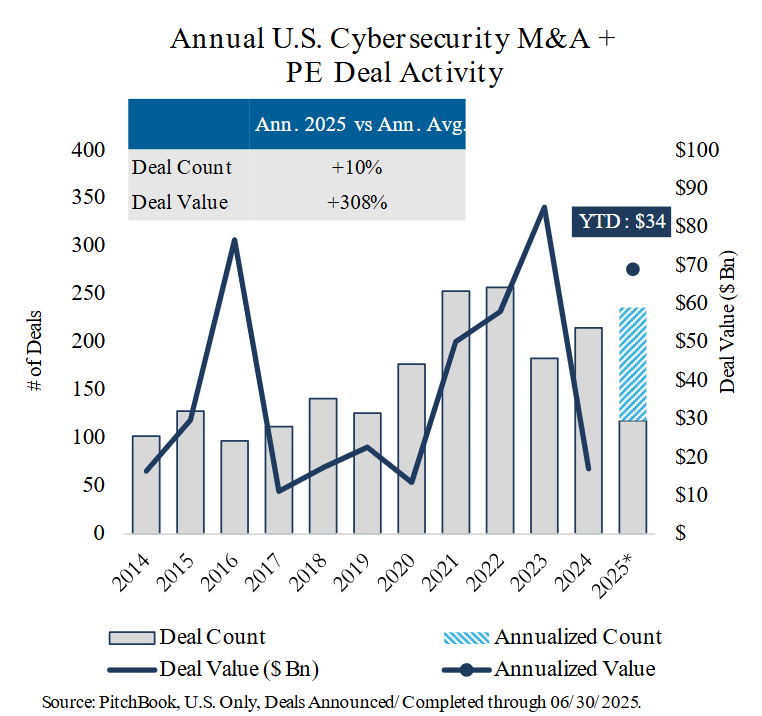
U.S. Cybersecurity M&A + PE Deal Activity
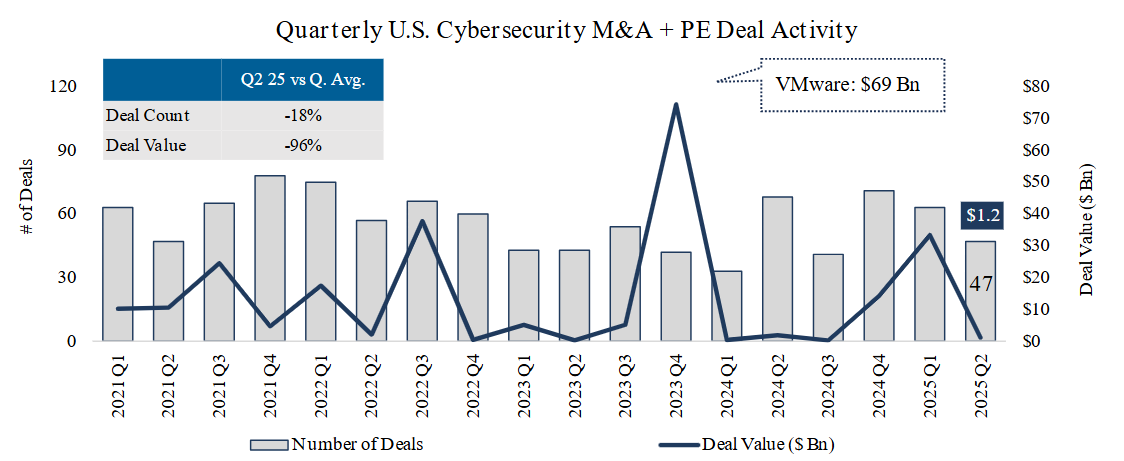
- Deal count: In Q2 2025, deal count fell below the prior quarter as well as the quarterly average of the past four years. However, strong volume in Q1 and healthy volume in Q2 bodes well for an elevated full-year deal count, as sector dealmaking tends to accelerate in H2.
- Deal value: In Q2 2025, deal value was muted, with no megadeals and many deals without disclosed values.
- Cumulative deal value: In 2023, cumulative deal value reached unprecedented levels due to several deals valued between $1 Bn – $5 Bn, along with Broadcom’s $69 Bn acquisition of VMware.
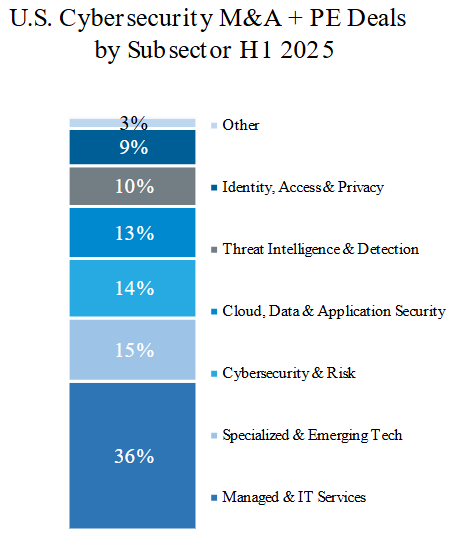
Top 5 U.S. Cybersecurity Deals by Size YTD
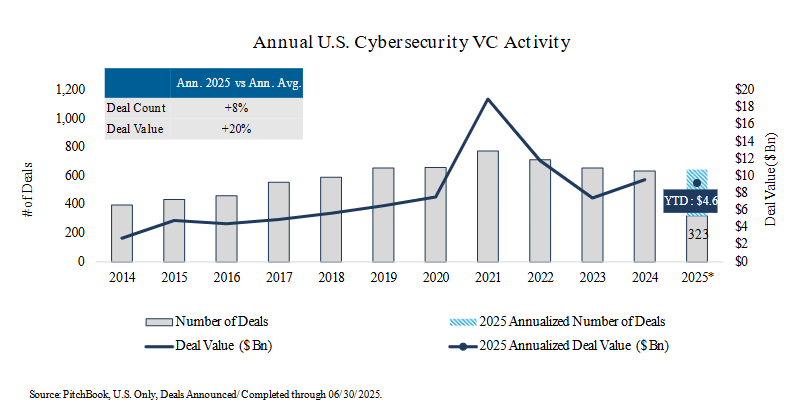
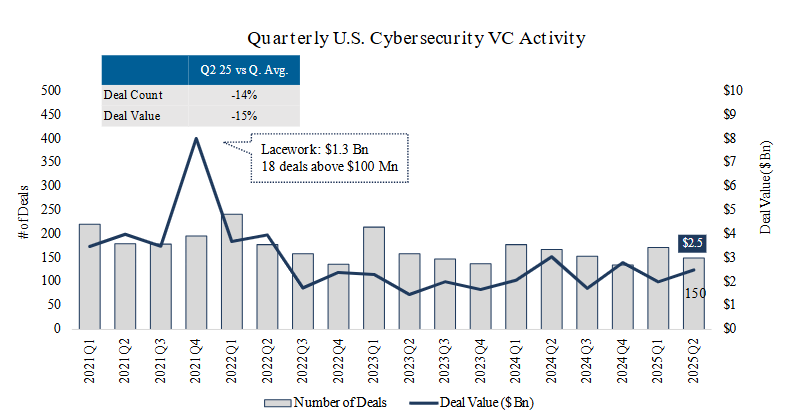
U.S. Cybersecurity VC Deal Activity
- Deal count: In Q2 2025 deal activity decreased from last quarter and is slightly below the quarterly average, mirroring the general wait-and-see mode of the broader market. If this pace is maintained, projected year-end 2025 deal count will be in line with last year, suggesting some cautious optimism for the rest of the year.
- Deal value: In Q2 2025, VC deal value increased compared to last quarter despite being slightly below the four-year quarterly average. The largest VC deal of Q2 was Cyera’s $540 Mn Series E funding round.
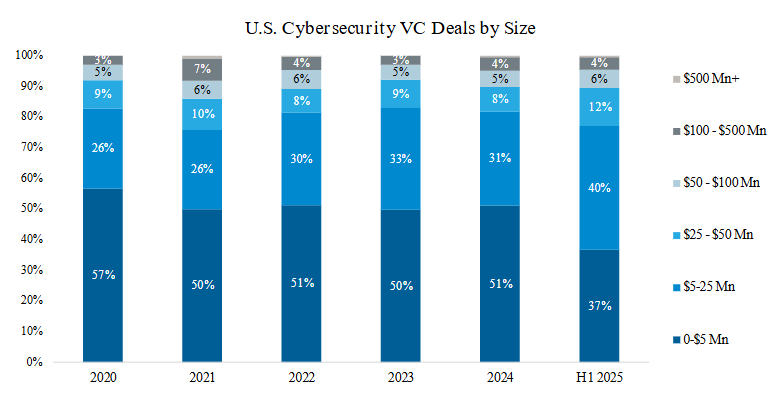
U.S. Cybersecurity VC Deal Size
- In H1 2025, the proportion of VC deals with disclosed deal values between $5-$25 Mn were 11 percentage points above the five-year average (2020-2024), while the proportion of deals smaller than $5 Mn decreased.
- The majority of deals with disclosed values in H1 2025 were below $25 Mn, in line with the five-year trend.
Top 5 U.S. Cybersecurity Deals by Size YTD
Public Company Financials
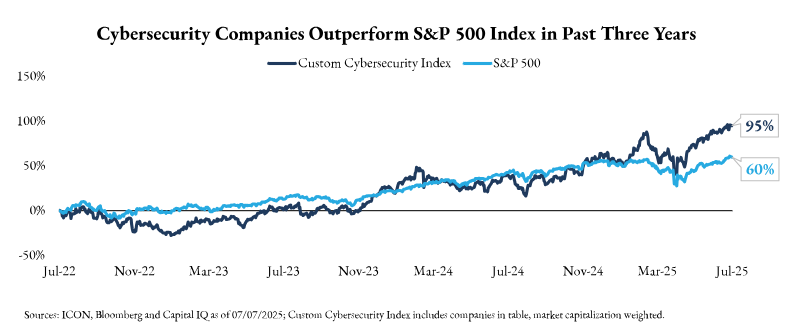
U.S. Cybersecurity Trends
M&A Dealmaking: M&A activity in the cybersecurity sector is expected to remain strong in 2025, driven by the growing need for comprehensive solutions amid the increasing prevalence and complexity of cyber attacks. It is likely that 2025 will continue to see consolidations between larger firms and niche players to enhance their capabilities or expand product offerings.
Venture Capital: VCs have been focused on proactive threat prevention, identity and cloud security, and regulatory alignment. As underlying technologies evolve and agentic AI reshapes everything from threat detection to team workflows, there is a shift in VC strategy to focus on proactive defense rather than reactive response. Early-stage funding investment in seed and Series-A start-ups continues to lead the funding landscape in 2025.
IPO: Driven by demand tailwinds that include escalating threats and digital sovereignty needs, there is cautious optimism for cybersecurity IPOs in H2 2025 despite high interest rates and tariff uncertainty. SailPoint’s IPO in February (valuing the company at $12.8 Bn), has set the stage for other mature cybersecurity firms to follow suit.
Industry Growth: Global cybersecurity spending is expected to surpass $1.75 Tn cumulatively between 2021 and 2025, with $459 Bn allocated in 2025 alone.
Zero-trust and cloud adoption have been popular due to increased demand in identity and access management and privileged access management as identity risks amid non-human identities increase.
Additionally, the industry will continue to seek out talent as there is a global shortage of an estimated 2.8 million cybersecurity professionals.
July 8, 2025 – Pinpoint
“Investors are placing larger, more selective bets — evidenced by eight rounds exceeding $100 million accounting for 55 percent of all Q2 funding. But macro headwinds persist, with ongoing tech layoffs and enterprise budgets under scrutiny. Success in the second half of 2025 will require cybersecurity companies to demonstrate clear value propositions, strong go-to-market execution, and measurable outcomes rather than flashy features.” – Founder and Managing Partner, Pinpoint.
May 20, 2025 – Palo Alto Networks
“The volume and complexity of threats are not slowing down either. Bad actors are using AI to move faster than ever. Recently, our Unit 42 team was able to simulate an entire ransomware attack in under 25 minutes using AI at every stage of the attack chain. That’s a staggering increase in speed, powered entirely by AI.” – CEO, Palo Alto.
May 2, 2025 – McKinsey & Company
“For many clients, cybersecurity is a ‘layered’ solution, in which a variety of different products and services leads to better security. The growing shortage of workers with cybersecurity skills makes organizations particularly dependent on layered services to compensate for the lack of talent available.”
March 11, 2025 – Secureworks
“I think in 2025 we’ll see more M&A and industry consolidation. I think there is still, when it comes to M&A, a lot of niche players [and] too much confusion in the marketplace. I think you’re going to still see M&A as a driving mechanism in 2025.” – Director, SecureWorks.
U.S. Cybersecurity Outlook
AI and Automation Integration: Generative and agentic AI are being leveraged to enhance threat detection, automate patching, and improve cloud security. The market is projected to grow at a 33.4% CAGR, reaching $40.1 Bn by 2030, fueled by AI’s ability to detect sophisticated threats, generate secure code, and accelerate DevSecOps cycles.1
Platformization and Consolidation: Experts predict continued M&A activity, with major companies consolidating smaller players to form comprehensive platforms, as demonstrated by Palo Alto’s acquisition of Protect AI in April. This trend is driven by enterprises seeking integrated solutions for endpoints, cloud workloads, and identity security.
Cloud Security and Zero-Trust Architecture: The shift to cloud-first strategies is accelerating demand for cloud security tools and zero trust frameworks, where identity and data protection is key. Companies like AWS, Microsoft, and Google are centralizing security in their ecosystems, while companies like Palo Alto and CrowdStrike are adapting their offerings to align with cloud-native and SaaS-based approaches.
Adversarial Adaptation: Organizations face a dynamic and evolving threat landscape, from deepfake impersonations to the development of highly sophisticated AI malware capable of adapting in real time to security protocols, making detection more difficult. Additionally, large language models (LLMs) are being exploited to automate large-scale social engineering attacks, enabling more convincing scams across email, messaging apps, and even virtual assistants. Notably, credential phishing attacks increased by 703% in the second half of 2024, largely due to the advent of AI.2 As deepfake and LLM attacks evolve, defenders must adopt proactive and real-time adaptive AI to stay ahead.
Military and Defense Sector Investment: Increased spending on cybersecurity by defense and military organizations is expected over the next five years due to evolving threats and zero-trust mandates. For example, the U.S. Coast Guard has updated its maritime security regulations recently by establishing minimum cybersecurity requirements for U.S.-flagged vessels. The Department of Defense now mandates zero-trust implementations, while companies like Shift5 expect it to become standard in aircraft systems by 2030.
Carveouts and Divestitures: Cybersecurity companies are carving out assets that no longer align with core offerings or address technological shifts. For example, WithSecure divested its cybersecurity consulting business to Neqst in February. Sector players are expected to continue to sell off non-core assets for strategic realignment amid the technological shift triggered by the advent of AI.
Tariff and Regulatory Implications
Potential Digital Services Tariff: The Trump administration called for a renewal of the digital service taxes (DST) investigation. A new tariff policy could draw more uncertainty to the future of cybersecurity companies, disrupting costs and pricing.
Digital Sovereignty: The push for digital sovereignty is driving demand for domestic cybersecurity solutions amid geopolitical tension.
1 SentinelOne Expert Call, 2Slash Next
[ad_2]